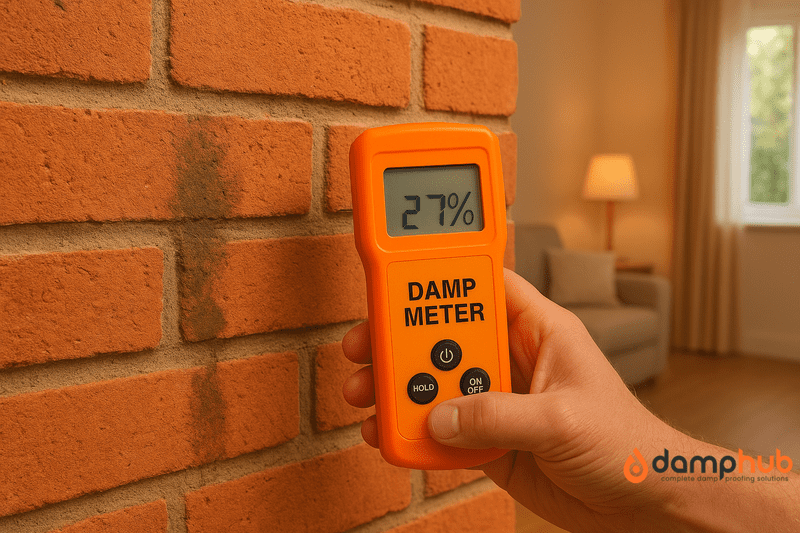
If you’ve ever noticed peeling paint, mould spots, or that musty smell creeping into your home, chances are that damp is behind it. But before you start stripping walls or spending money on treatments, you need to know how serious the problem is. That’s where a damp meter comes in.
So, what is a damp meter? Simply put, it’s a handheld tool designed to measure the moisture content in walls, floors, or timber. Surveyors, builders, and even cautious homeowners use them to check if a surface is holding more water than it should. Without one, you’re often just guessing whether damp is the real culprit behind stains or damage.
Types of Damp Meters
Not all damp meters are built the same. The two main types are:
- Pin-type damp meters – These have sharp probes you push into the material. They measure electrical resistance to estimate the amount of moisture present.
- Pinless damp meters – These use sensors placed against the surface, often using radio waves, to detect moisture levels without piercing the material.
Each has its place. Pin meters are great for timber and give direct contact readings. Pinless meters are quicker for checking walls and broader areas without leaving marks.
How Does a Damp Meter Work?
At its core, a damp meter measures changes in electrical resistance or conductivity caused by moisture. Water conducts electricity, so the more conductive a material is, the more current flows through it.
- Pin meters send a small current between the probes; resistance levels tell the meter how wet the material is.
- Pinless meters scan beneath the surface using electromagnetic signals, giving a moisture estimate.
So, when asking “what is a damp meter and how does it work?”, the answer is: it’s essentially a diagnostic tool that converts electrical reactions into a readable scale.
How to Use a Damp Meter
Using a damp meter is fairly straightforward, but accuracy depends on technique:
- Choose the right meter – Pin for timber, pinless for walls.
- Calibrate if needed – Some models need a quick zeroing step.
- Test multiple spots – Damp often spreads unevenly.
- Compare against dry areas – Always take a baseline reading.
The key is not just using the damp meter once but checking across different parts of the wall, floor, or beam to see patterns.
How to Read a Damp Meter
Reading a damp meter properly avoids false conclusions. Most devices show results in percentages (%MC for moisture content) or on a colour-coded scale.
- 0–15% MC – Normal, safe levels.
- 16–20% MC – Borderline, may indicate early damp issues.
- 20%+ MC – High moisture; damp is present, and action is needed.
Some meters show a traffic-light system: green (safe), amber (borderline), and red (damp). Understanding these ranges makes the difference between spotting harmless surface moisture and diagnosing a real damp problem.
What Is a Normal Damp Meter Reading?
In UK homes, a normal damp meter reading for walls is usually below 15% moisture content. Timber should ideally sit around 12–15%, though slight variations are normal depending on season and ventilation.
If readings are consistently higher than 20%, especially in walls, it often points to condensation, rising damp, or water ingress.
For more guidance, read our other related post: What Percentage Damp Is Acceptable In Walls?
How Accurate Are Damp Meters?
Damp meters are useful, but not flawless. Pin meters tend to be more precise for timber, while pinless models sometimes overestimate moisture in dense masonry.
Accuracy depends on:
- The material being tested (brick, plaster, or wood).
- Correct calibration.
- Environmental factors like salts in old walls.
Professionals often use damp meters as an indicator tool, not as absolute proof. A reading suggests damp, but further inspection is needed to confirm the cause.
What Affects Damp Meter Readings?
Several factors can skew results:
- Surface salts – Common in old brickwork, they can trigger false “damp” readings.
- Temperature – Cold surfaces may appear wetter.
- Depth – Pinless meters can only scan a few millimetres deep.
- User error – Poor contact or testing only one spot can mislead.
That’s why knowing what is a damp meter and how to interpret it is more important than just owning one.
How Do I Reset My Damp Meter?
We’ve answered “what is a damp meter”, but how about resetting or recalibrating it? Recalibrating a damp meter is the process of checking and adjusting the meter’s settings to ensure it provides accurate and reliable moisture readings.
It involves comparing the meter’s measurements to known standards to minimise errors and confirm the device is giving correct measurements, which is crucial for making informed decisions in industries like construction, agriculture, and manufacturing.
The exact method depends on whether you have a digital or analogue model.
1. Digital Damp Meters
Most modern models include a reset or calibration function.
- Locate the reset button – Often marked “CAL” or “ZERO.”
- Hold the probes in free air – Make sure they’re not touching any surface.
- Press and hold reset – Wait until the screen zeros or stabilises.
- Use a calibration block if supplied – Some high-end meters include one for precision.
2. Analogue Damp Meters
Older or manual devices require a different approach.
- Check against a known dry sample – e.g., a dry piece of timber.
- Adjust the dial/screw – Turn until the meter reads zero on the dry material.
- Repeat periodically – Analogue meters drift over time and need more frequent checks.
3. General Tips
- Always reset indoors at room temperature for consistency.
- Repeat the process every few uses to avoid drift.
- If your meter doesn’t hold calibration, the battery may need replacing.
Final Thoughts
So, what is a damp meter really? It’s not just another DIY gadget — it’s your first line of defence against hidden moisture problems. By spotting abnormal readings early, a damp meter helps you tackle condensation, leaks, or rising damp before they spiral into costly repairs.
If you’re considering buying one, remember that not all damp meters are created equal. Some are designed for timber, others for masonry, and a few come with handy extras like backlit displays or calibration blocks. To make choosing easier, we’ve tested and compared the Top 10 Best Damp Meters for Walls, Floors & Timber. Check out our full review before you buy.
What is a Damp Meter? Frequently Asked Questions

-
How to reduce damp meter reading?
Fixing the root cause is key – improve ventilation, repair leaks, or add a damp-proof course. Simply trying to “dry out” a wall without solving the source won’t work long term.
-
Is it worth buying a damp meter?
Yes, especially for landlords, DIYers, or anyone living in older properties. It helps spot problems early before they escalate.
-
Can a moisture meter be wrong?
Yes. They don’t always distinguish between actual water and salts or surface condensation.
-
How to know if a moisture meter is accurate?
Test it on a known dry piece of timber or wall section. If it reads low there, it’s likely calibrated correctly.